反转链表
不要跳进递归,而是利用明确的定义来实现算法逻辑。你的脑袋有几个栈啊!
基本上,所有的递归问题都可以用递推公式来表示。有了这个递推公式,我们就可以很轻松地将它改为递归代码。。所以,遇到递归不要怕,先想递推公式。
递归是一种关于某个重复动作(完成重复性的功能)的形式化描述。具体点讲,如果一个问题 A 可以分解为若干子问题 B、C、D,你可以假设子问题 B、C、D 已经解决,在此基础上思考如何解决问题 A。
将问题抽象化,可以将问题抽象为f(n)(或者其他的数学符号), 然后用f(n)代表欲求的问题,然后去发现和子问题(比如f(n-1))的递推关系!(这一点在写动态规划的时候特别有用,其实动态规划就是记忆化的递归!)
递归函数是带语义的,但是记住一个递归函数只有一个语义,如果在写递归函数实现的时候,发现出现了多个语义,需要对新出现的语义重新定义一个函数!
作者:Chuancey
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/fan-zhuan-lian-biao-lcof/solution/kan-bu-dong-di->gui-de-kan-guo-lai-xi-wan-1akq/
进入正题:反转链表题
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int left, int right) {
if(left==1) return reverselist(head,right);
head->next = reverseBetween(head->next,left-1,right-1);
return head;
}
ListNode* reverselist(ListNode* head,int n)
{
if(n==1){
last2 = head->next;
return head;
}
ListNode* last = reverselist(head->next,n-1);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = last2;
return last;
}
private: ListNode* last2;
};
|
反转链表的思路是 全反转 → 从1到n 的反转 → 从m到n的反转
全反转的代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| reverse(ListNode* head){
if(head==NULL||head->next==NULL){
return head;
}
ListNode* last = reverse(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = NULL ;
return last;
}
|
1到n:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| ListNode* last2;
reverseN(ListNode* head, int n)
{
if(n==1){
last2 = head->next;
return head;
}
ListNode* last = reverseN(head->next,n-1);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = last2;
return last;
}
|
和全反转相比,要区分 last: 反转的头结点(原最后结点) , last2:反转的尾结点的next(原起始结点的next)

m到n:照顾头结点,
1
2
3
4
5
6
| ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int left, int right) {
if(left==1) return reverseN(head,right)
head->next = reverseBetween(head->next,left-1,right-1);
return head;
}
|
拓展:
同样的问题有个迭代的法子:
全反转:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| ListNode* prev = nullptr;
ListNode* curr = head;
while(curr)
{
ListNode* n = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
|
mn反转(头插法):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| class Solution {
public:
ListNode *reverseBetween(ListNode *head, int left, int right) {
ListNode *dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);
dummyNode->next = head;
ListNode *pre = dummyNode;
for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++) {
pre = pre->next;
}
ListNode *cur = pre->next;
ListNode *next;
for (int i = 0; i < right - left; i++) {
next = cur->next;
cur->next = next->next;
next->next = pre->next;
pre->next = next;
}
return dummyNode->next;
}
};
|

此时把线拉直就是变化后的效果。
反转一组固定长度为K的链表
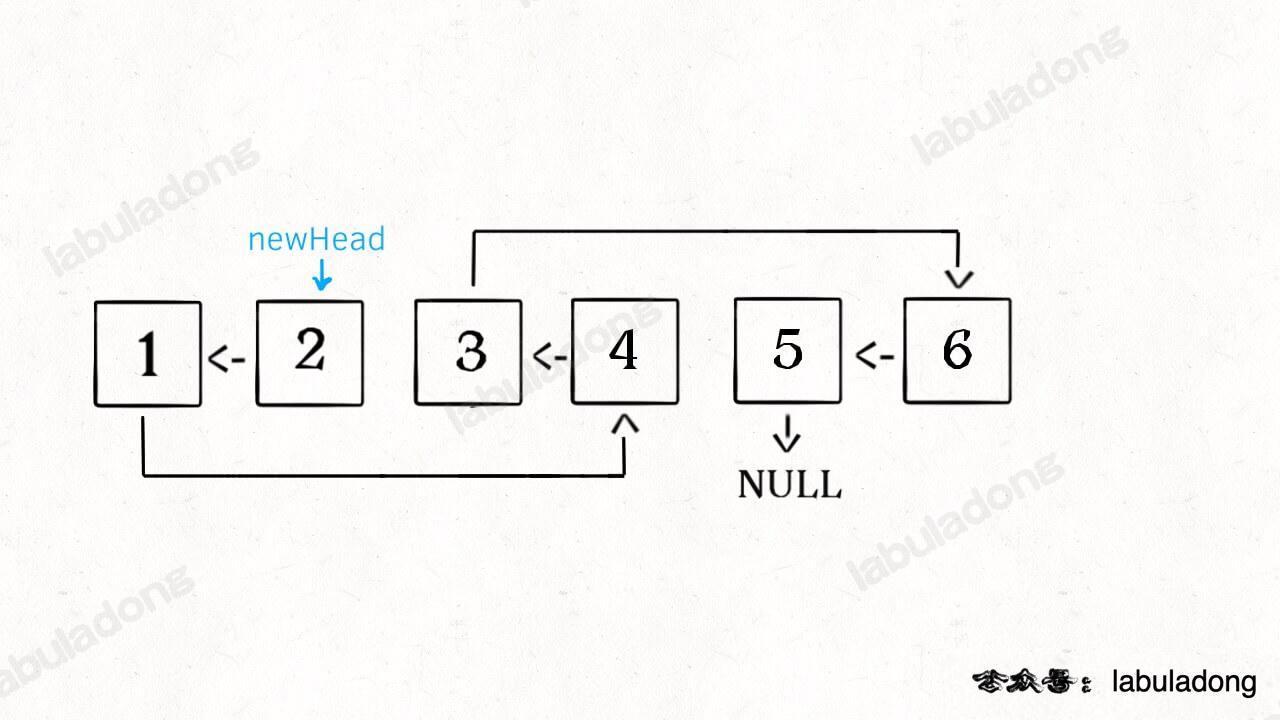
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
if(!head) return head;
ListNode* a = head;
ListNode* b = head;
for(int i=0;i<k;i++)
{
if(!b) return a;
b=b->next;
}
ListNode* newHead = reverse(a,b);
a->next = reverseKGroup(b,k);
return newHead;
}
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* a,ListNode* b)
{
ListNode* cur = a;
ListNode* pre = NULL;
while(cur!=b)
{
ListNode* n = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = n;
}
return pre;
}
|
判断回文链表
思路一:
链表不能直接走,但可以借助后序遍历的思路,左指针为头结点,后序遍历比较
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
left = head;
return traverse(head);
}
bool traverse(ListNode* right)
{
if(right == NULL) return true;
bool res = traverse(right->next);
res = res&&(left->val == right->val);
left = left->next;
return res;
}
private:
ListNode* left ;
};
|
思路二:反转链表后模仿双指针(从中间向两边)
三步走:
- 找到中间结点:快慢指针
- 反转链表
- 前半部分和后半部分逐个对比。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* left = head;
ListNode* right = midpointer(head);
right = reverse(right);
return compnode(left,right);
}
ListNode* midpointer(ListNode* head){
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while(fast!=NULL&&fast->next!=NULL)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
if(fast!=NULL) slow=slow->next;
return slow;
}
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* head){
ListNode* pre = NULL;
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur!=NULL)
{
ListNode* n = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = n;
}
return pre;
}
bool compnode(ListNode* left,ListNode* right){
while(right!=NULL)
{
if(left->val!=right->val) return false;
left = left->next;
right = right->next;
}
return true;
}
};
|


